Q.1:Define:

 – Standard kilogram : The mass of a cylinder made of platinum and iridium alloy of specific dimensions kept at
– Standard kilogram : The mass of a cylinder made of platinum and iridium alloy of specific dimensions kept at 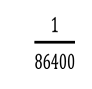 1/ 86400 of the average solar day.
1/ 86400 of the average solar day. 
 – Displacement : The change in the position of object ‚ or the length of the straight line segment in a given direction between the starting point and the end point .(vector quantity)
– Displacement : The change in the position of object ‚ or the length of the straight line segment in a given direction between the starting point and the end point .(vector quantity)